IT System and Cybersecurity
With the increased complexity and connectivity of our critical infrastructure as an effort to shift toward digital transformation, the Bank places the utmost importance on IT system and cybersecurity to ensure stability and security of our systems and operations, and to mitigate cybersecurity risks that could result in financial and reputational loses. IT system and cybersecurity are the foundation of the Bank’s infrastructure that secure and maintain our customers’ trust and confidence.
The Bank has a clear management structure with dedicated governing board and management committees for information technology and information security. For a board-level committee, IT Oversight Committee supervises the formulation of IT and cybersecurity strategies, policies, and operating plans, and oversees cybersecurity risks. For a management-level committee, IT Non-Financial Risk Committee manages information security and cybersecurity management to ensure maximum safekeeping of our systems and operations. The Board of Directors appoints the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) to protect our customers’ sensitive financial information. The CISO’s role and responsibilities include setting the direction and strategy of the Bank’s cybersecurity management, establishing end-to-end security technologies and processes, and minimizing information security-related risks. To make sure our practice complies with our policies and standards, the audit function conducts internal audits of the design and effectiveness of IT infrastructure and information security management systems and give recommendations for further improvement. Additionally, the Bank seeks independent external certification of ISO 27001 and Swift Customer Security Controls Framework.
The IT infrastructure and system are the backbone of the Bank. The Bank established Cyber and Digital Risk Management Policy which is internally available and enforced to all employees. The policy details the Bank’s management approach to ensure integrity and protection of data, focusing on information risk management and establishment of minimum standards to protect the Bank’s data and information of all business units as well as requirements for third parties. The IT infrastructure and system are constantly being checked, updated, and maintained to ensure its functionality and effectiveness, and continuous improvement of information security systems. The policy clearly defines roles and responsibilities of all individuals in the Bank ranging from the Board of Directors, senior executives, all IT asset owners, and end users. On an annual basis, we conduct information security-related business continuity plans (BCP) to test incident management and target recovery time from potential disruptions that may occur. We conduct third-party vulnerability analysis (penetration testing) including simulated hacker attacks. We continuously improve the stability of our technology systems to withstand potential threats so that they are available to service our customers.
The Bank has systems in place to protect against, detect, and respond to cyber-attacks. Our cybersecurity framework is adopted from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which consists of five key components; identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover, with layers of security networks to ensure maximum protection. We regularly monitor our performance to make sure that we comply with the framework and issue quarterly reports to the board-level committee. Moreover, we conduct incident response test annually to test our security system, understand our lacking areas, and further enhance it.
To strengthen our cyber-attacks preventative measures, the Bank established two minimum standards; Cybersecurity and Resilience Minimum Standard and IT Security Monitoring Minimum Standard. Cybersecurity and Resilience Minimum Standard aims to ensure active and passive monitoring of cybersecurity and resilience and that they are conducted effectively in a timely manner and that the Bank’s IT system is designed and implemented in such a way that they are not affected by disruptions. This was an effort in preparation for current and future cyber threats, including unprecedented, unpredictable, and unexpected cyber threats. IT Security Monitoring Minimum Standard’s purpose is to outline the control requirements related to IT security monitoring activities, which are comprised of technical state compliance monitoring, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, secure code review and security event monitoring.
Building our people’s capacity in this area is as crucial as strengthening our infrastructures. The Bank has developed e-learnings on cybersecurity to create awareness and understanding, and also educate employees on how to prevent cyber-attack and cyber-threats. It is mandatory for all employees to complete trainings on information risk awareness and management. The aim was to raise awareness on informational risks and how to safeguard from cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and social media. Our Board of Directors also received a cybersecurity awareness training by an external expert. The training covered key principles of cybersecurity and cyber-risk management, security landscape, globalization of cybercrime, data breach statistics, and different types of cyber threats.
Data Privacy
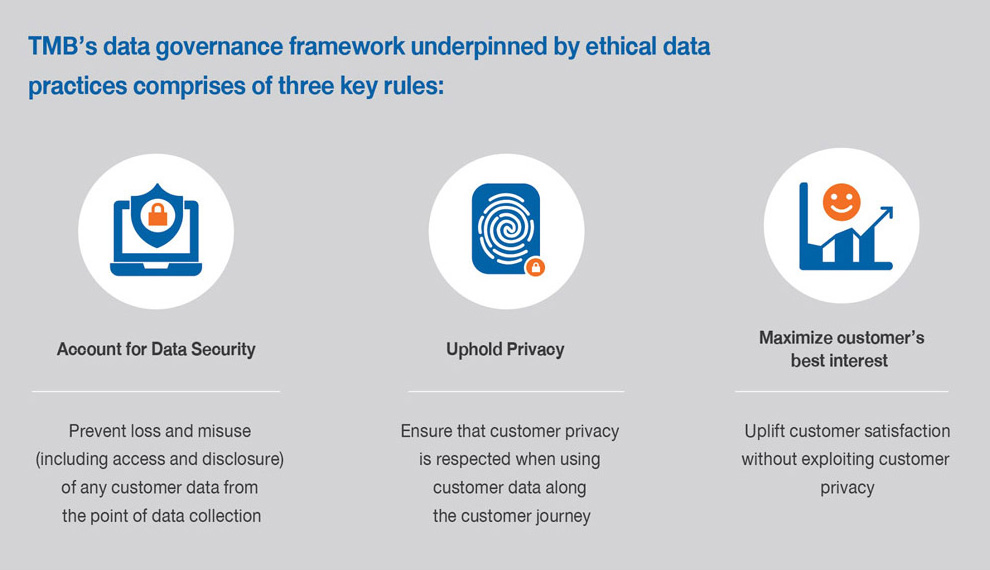
In this digital age, there is a massive amount of consumer data being generated, collected and shared rapidly in both structured and unstructured format such that data proliferation and exposure to cybersecurity risks have been magnified substantially. Since customer data provides us meaningful insights into product innovation and development as we continue to address the needs of our customers, data privacy will remain the Bank’s top priority. The Bank places great importance on security of our customers’ personal data and is committed to protecting the privacy and confidentiality of customer’s personal information in compliance with the Bank’s data governance framework and relevant laws and regulations.
Financial institutions have been entrusted with copious amounts of data from customers for which traditional governance frameworks and risk mitigation strategies have proved insufficient. To that effect, data governance is necessary to handle and process data securely and effectively as it is imperative to establish an organization-wide governance structure. In view of this, the Bank has instituted a proper data governance structure founded upon the three-tiered approach and regulated through the organizational structure with explicit roles and responsibilities. Consequently, this is steered by the Bank’s top management to ensure alignment across business operations through regular meetings. The Board of Directors holds the ultimate responsibilities for bank-wide risk management. The Bank appoints the Head of Compliance as the Data Protection Officer (DPO) to advise and monitor bank-wide practices in an independent manner, while acting as the focal point for data protection supervisory authority on data privacy matters in order to successfully manage the quality of our data in a sustainable manner as well as overseeing data privacy risk management. The DPO reports to the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) with a dotted line to the CEO, ensuring that the privacy management system is embedded in group-wide risk management. Most importantly, data governance is a fundamental constituent of security to which the Bank’s intentions of instituting appropriate security measures are to detect, investigate, manage and deter potential security threats or suspicious activities. These measures consist of cybersecurity; role-based access control; inspection systems in the IT environment; monitoring reaction and containment efforts; and data breach handling procedures.
With our approach to data privacy, the Bank’s implementation of data privacy mechanism is to safeguard the use of customer data and ensure its compliance with regulatory and legal requirements. Notably, customers must give explicit consent for data use and are entitled to withdraw their consent at any point in time. The coverage of the Bank’s data privacy practices applies to the Bank’s entire operations and also extends to our supply chain where the supplier code of conduct and outsourcing policy incorporate data privacy requirements; predominantly a more stringent vendor selection criteria and requirement of signatures on the data management addendum to prevent unauthorized access, disclosure or data breach.
Strengthening employee awareness on data privacy conduct through communication and education is undoubtedly an effective means to establish a strong presence of data privacy management in the Bank. The Bank trained employees on relevant risks related to data protection (e.g. role-based access control, data leakage), and topics concerning information risk management, safeguard against cyberattacks, social media, data leakage and data privacy.
With colossal amount of data collected enmasse by the Bank as part of its daily operations, data quality is equally important to data governance and data privacy as it assesses whether the information can serve its purpose in a particular context. For this reason, the Bank places emphasis on data quality (determined by its accuracy, timeliness, completeness, and reliability); and data traceability (employing metadata to facilitate full data visibility across different groups at a granular level). To this end, the system of checks and balances are in place as it warrants proper implementation of data management in accordance with internal regulations and full compliance with relevant laws and regulations; notably, Personal Data Protection Act B.E. 2562 (PDPA), Bank of Thailand’s Market Conduct’s minimum standards of data privacy, and Cyber Security Act B.E. 2562.
Managing and safeguarding customer data to ensure maximum security is one of ttb’s top priorities and the Bank has zero tolerance to any violations. This operational procedure details the actions ttb takes when there is a case of breach. The Bank has Disciplinary Regulation, Action and Punishment Procedure that includes items: Work discipline that the Bank expects from employees and what ttb considers as violations, Punishment, Investigation is conducted with confidentiality, fairness and integrity to ensure the cases are substantial with real evidence, Case dismisses, Appeal against disciplinary action, Authoritative person to make decisions on the punishment, and Indemnification.
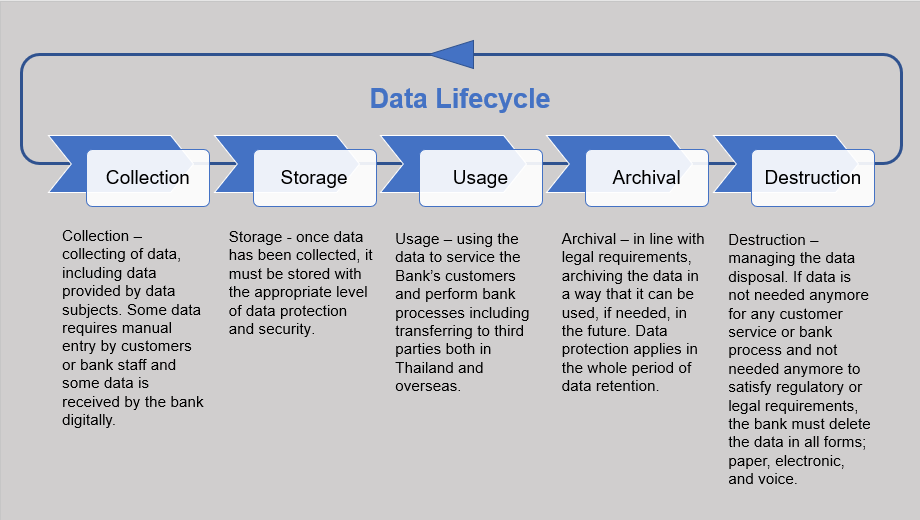
To ensure the standardization of data management, the Bank has in place data lifecycle management, a comprehensive approach to managing the flow of data from collection and storage to the time when it becomes no longer needed and is destroyed. The data lifecycle management consists of five phases as shown in the diagram. When the Bank processes personal data, data privacy and protection is applied. Furthermore, data minimization and purpose limitation will be taken into consideration for data processing activities; collection, usage, and disclosure. The Bank ensures that in every stage of the data life cycle, all relevant personnels comply with our policies and procedures. Internal Audit, Business Operational Risk Management, and Corporate Operational Risk Management conduct annual control testing on data management matters. Particularly, Internal Audit, as the 3rd line of defense, provides and independent assurance of the design and effectiveness of internal controls.